Speech-to-Text Services: ASR vs STTS

Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is technology or software that automatically converts spoken language into text, which can be done in real-time.
Speech-to-Text Services: Provider Confidentiality

Professional STTS providers are accountable to maintain confidentiality in all situations.
Speech-to-Text Services: Hiring STTS Providers

STTS providers can be hired as staff members, independent contractors, or be contracted through an agency. When evaluating qualifications, gather information about the provider’s skills, credentials, and experience working in various settings prior to hiring.
Speech-To-Text Services (STTS)

Speech-To-Text Services is an umbrella term for the different types of real-time captioning services where spoken and auditory information are translated into text by a trained professional.
Root Causes and Key Impact Areas
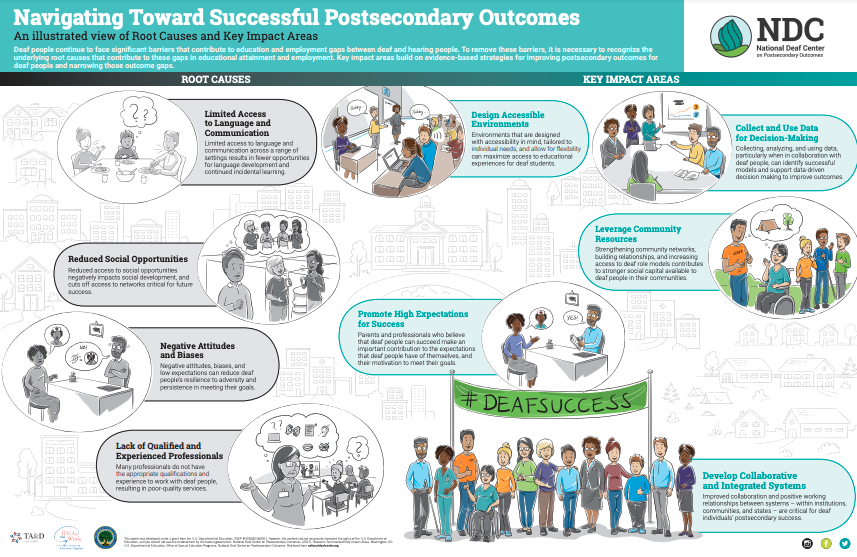
Root causes and key impact areas.
Remote Services Poster

Deaf students enrolling in colleges across the country are on the rise and securing access services can be difficult for institutions. Remote interpreting and speech-to-text services are viable options for institutions experiencing: shortages of qualified providers, specific interpreting or captioning needs for a course, or last-minute requests for urgent situations.
Interpreting: Interpreters and Confidentiality

Interpreters adhere to a Code of Professional Conduct (CPC) upheld by the Registry of Interpreters for the Deaf (RID) with the first tenet focusing on confidentiality. This tenet notes that interpreters must protect consumers’ privacy and that any content information discussed between all parties must not be shared.
Interpreters and Confidentiality
These resources contain more in-depth information about topics related to interpreting.
Interpreting: Coordinating Interpreting Services

When arranging interpreting services, you can ensure effective communication access by hiring qualified interpreters, keeping interpreting consistent, and checking in regularly with the deaf person.
Interpreting
Interpreting eases effective communication between hearing and deaf people, and is commonly used in education, employment, healthcare, legal settings, entertainment, and more.
Deafverse: Teacher Strategy Guide

This book offers guidance before, during, and after the game, including learning objectives as well as a summary of the story and characters. You will also find important vocabulary, activity guides for each chapter, and other supplemental materials
Deafverse: Player Strategy Guide

Deafverse is a game about the deaf experience. Sometimes players need to step back and look at the things happening to them in life. That’s why they should get their own strategy guide! This guide uses examples from Deafverse so players can think about what they would do in these situations.





