Home » Resources » Research & Data » Rural Deaf Experiences: Employment and Educational Attainment Data
Rural Deaf Experiences: Employment and Educational Attainment Data

Our data indicate that employment and educational attainment differences persist between hearing and deaf people (Bloom et al., 2024). These differences are more significant in rural areas. Rural deaf people may experience unique and additional challenges, such as a lack of resources and tailored support services. For example, deaf people in rural areas are nearly twice as likely as hearing people to lack internet access (13.8% vs. 7.6%). These statistics indicate the importance of addressing challenges to higher education for deaf people in rural areas, as education plays a crucial role in improving employment outcomes.
Nearly a quarter of deaf adults live in rural areas, a significantly higher rate than hearing people.
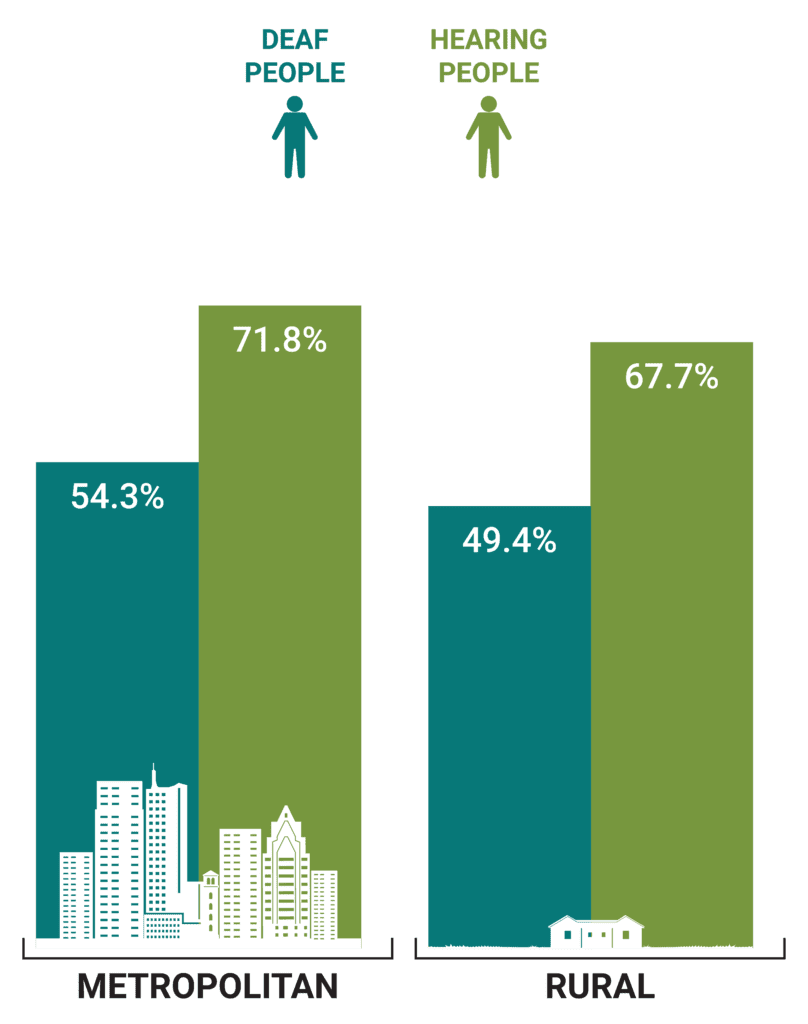
Employment by Group
Nearly a quarter of deaf adults live in rural areas, a significantly higher rate than hearing people.
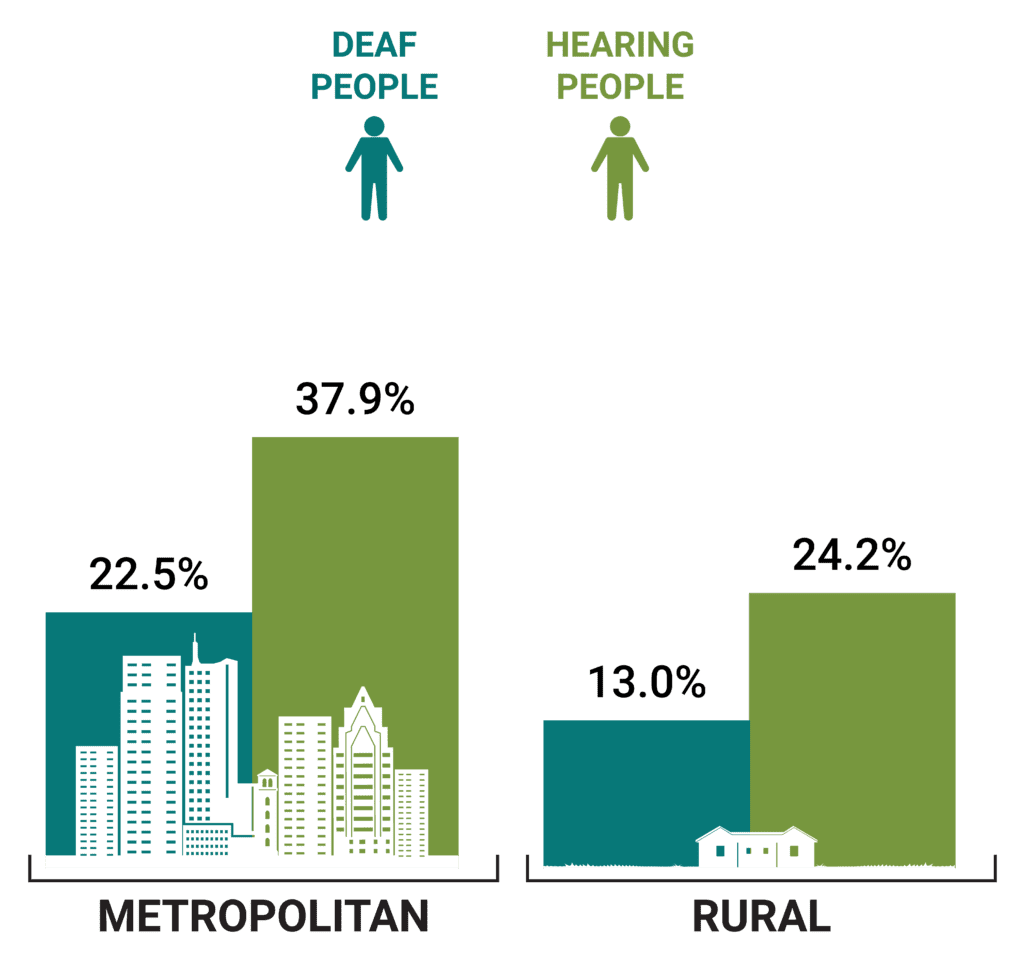
Bachelor’s Degree or Higher
Metropolitan deaf people are almost twice as likely as rural deaf people to have a bachelor’s degree or higher.
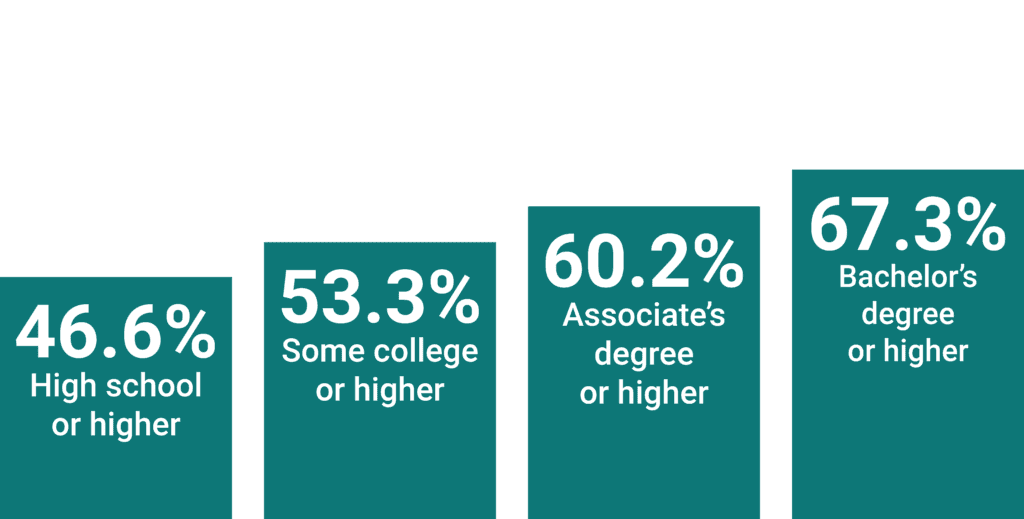
Employment by Educational Attainment
In rural areas, the employment rate of deaf people increases with educational attainment.
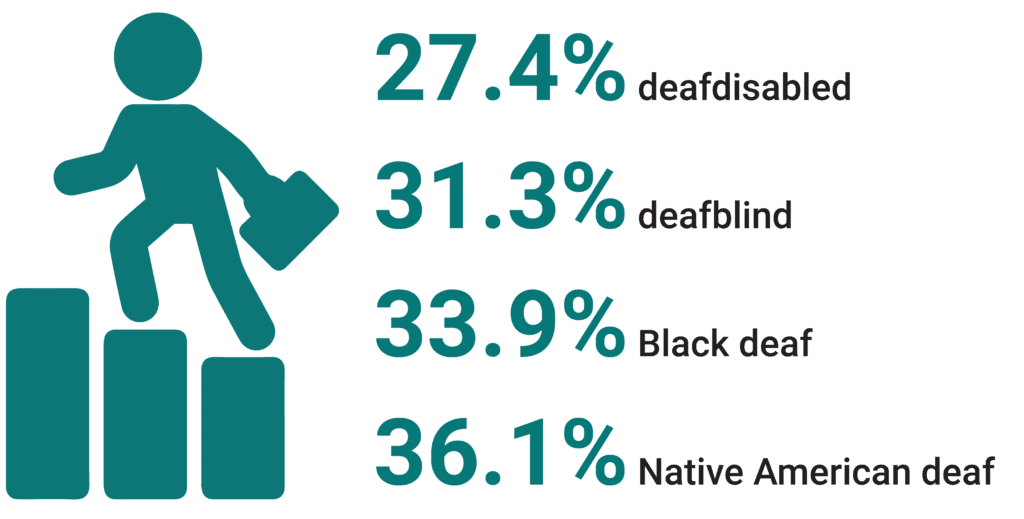
Table 1. Employment Rates by Deaf Groups in Rural Areas
Employed | Unemployed | Not in Labor Force | |
|---|---|---|---|
No disability | 68.0% | 3.4% | 28.6% |
Deafblind | 31.3% | 3.5% | 65.2% |
Deaf with disability | 27.4% | 3.6% | 69.0% |
Table 2. Employment By Gender
Deaf Men | Deaf Women | |
|---|---|---|
Metropolitan Areas | 57.9% | 49.1% |
Rural Areas | 51.8% | 43.9% |
Table 3. Employment by Race & Ethnicity
Rural Areas | Metropolitan Areas | |
|---|---|---|
Asian deaf | 50.2% | 55.4% |
Black deaf | 33.9% | 42.0% |
Latine deaf | 46.8% | 53.7% |
Multiracial deaf | 43.3% | 50.3% |
Native American deaf | 36.1% | 42.1% |
White deaf | 51.1% | 57.1% |
Table 4. Educational Attainment by Area
Education Level | Hearing Status | Metropolitan Areas |
|---|---|---|
High school or higher - DEAF | 85.1% | 83.6% |
High school or higher - HEARING | 90.1% | 86.4% |
AA or higher - DEAF | 32.2% | 22.6% |
AA or higher - HEARING | 46.9% | 34.9% |
Some College or higher - DEAF | 55.5% | 45.6% |
Some College or higher - HEARING | 66.3% | 56% |
BA or higher - DEAF | 22.5% | 13% |
BA or higher - HEARING | 37.9% | 24.2% |
MA or higher - DEAF | 8.15% | 4.4% |
MA or higher - HEARING | 14.3% | 8.4% |
Figure 1: Educational Attainment by Employment in Rural and Metro Areas
The data in this report comes from the 2018-2022 American Community Survey (ACS), which is a yearly survey conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. It gives us the most up-to-date information about education trends for deaf people in the United States. We used survey participants who identified as deaf or having serious difficulty hearing to represent the deaf population in our analyses. These estimates are based on a sample of 12,181 deaf people between the ages of 16 and 24 from 2018 to 2022. For additional details, please refer to our FAQs page that provides more information about the ACS data.